Types of Flying Bugs and Insects (With Pictures) – Identification Guide

Flying bugs and insects come in all shapes and sizes. Identifying species of flying insects and bugs in your home is vital to recognize harmless, venomous, and disease-carrying pests. Also, in your garden, flying insects can inflict a nasty sting or damage your ornamental flowering shrubs. However, not all winged bugs and insects are dangerous. Many insects that fly perform vital tasks such as pollinating flowers or feeding on plant-destroying pests.
This article is a comprehensive guide to common flying bugs and insects. Some of these winged creatures are recognized as flying pests. However, it’s a good idea to know which flying insects to attract to your yard to enhance biodiversity and protect insect populations.
Insects vs. Bugs
Insects are animals in the class Insecta with six legs, two antennae, and three body segments—a head, thorax, and abdomen. Flying insects can include flies, butterflies, wasps, bees, grasshoppers, and beetles. On the other hand, true bugs are a specific type of insect. They belong to the order Hemiptera.
The primary difference between bugs and insects is that bugs suck juices from plants. They use their straw-shaped mouth to pierce plants and feed on sap, juices, or other insects. Examples of true bugs include stink bugs, aphids, whiteflies, water bugs, and bed bugs.
So, all bugs are insects—but not all insects are bugs. This is similar to how ants are insects, but referring to all insects as ants is not correct. However, it gets confusing because some insects have the common name bug—but they are not true bugs. For example, ladybugs and June bugs are types of beetles.
And it’s good to remember that spiders are not types of insects but are crawling eight-legged creatures in the class Arachnida.
How to Identify Flying Insects
To identify flying insects, you should observe their behavior, shape, size, and habitat.
Observe the flying insect’s behavior. Some flying insects like wasps and bees become aggressive if you annoy them. However, you may see harmless butterflies on flowers. Some insects are attracted to light when it’s dark.
Look at the flying insect’s features. All flying insects are identified by common characteristics—two or four wings, six legs, and a segmented body. However, the colorful wings of some insects like butterflies or moths help to identify the species. Other winged insects have transparent wings.
Examine the flying insect’s shape. The best way to identify flying insects is by their shape. For example, bees and wasps are small with oval bodies. On the other hand, dragonflies have long colorful bodies, and butterflies and moths have larvae-like bodies and large wings.
The Most Common Flying Insects
Common flying insects include bees, wasps, flies, mosquitoes, butterflies, moths, beetles, and dragonflies. Even some ants and termites can fly when they need to leave their colonies. In most cases, it’s best to avoid killing flying insects unless they become a pest in the house or your plants.
The Most Common Flying Insects in the House
Common flying insects in the home include types of flies such as drain flies, fungus gnats, fruit flies, and house flies. These small brown or black flies are attracted to damp conditions or decaying organic matter. Depending on the climate, cockroaches can be common flying insects in the house that can become a pest.
Many types of houseflies and cockroaches are also disease carriers. Therefore, you should take steps to eliminate flies from your home. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diseases associated with household flies include E. coli, typhoid, cholera, and diarrhea.
Types of Flying Bugs and Insects (with Pictures) — Identification
Let’s look in more detail at the identification traits of common bugs and insects with wings and that can fly.
Bees (Anthophila)
Bees are common flying insects that are seen throughout the summer as they fly between flowers, pollinating them and collecting nectar. Most species of bees have identifiable black and yellow stripes and fuzzy bodies. However, various distinguishing features help identify individual bee species. For example, a bumblebee has a stout, furry body, whereas a honeybee has a slender, smooth abdomen.
Here are identifying features of common types of bees.
Honey bee (Apis)
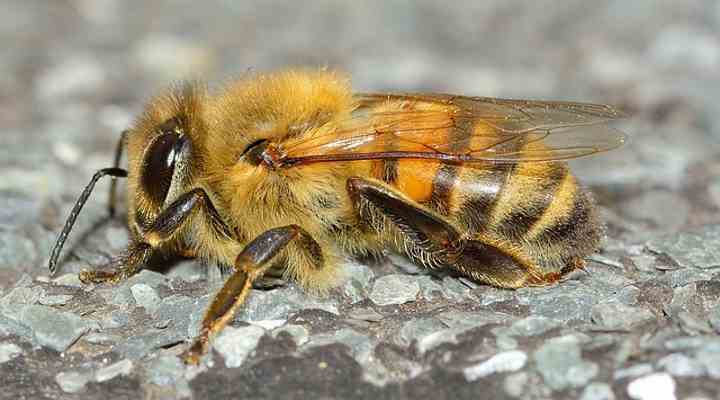

The Western honey bee (Apis mellifera) has three pairs of fuzzy dark legs, a pair of antennae, and two pairs of wings
The common western honeybee (Apis mellifera) is a flying insect with black and orange-yellow stripes on its body, a fuzzy head, thorax, and a smooth, slender abdomen. The honeybee’s hairy legs are used to help transport pollen back to the hive. Unlike types of wasps, honey bees are relatively docile and not aggressive.
These winged insects, which are also called European honey bees, are the primary bee species used for honey production. Yellow and brown striped honeybees usually grow 0.5” (13 mm) long.
Although there are over 20,000 bee species in the world, there are only eight honey bee species. These honey-producing insects in the genus Apis include the eastern honey bee (Apis cerana), the giant honey bee (Apis dorsata), and Koschevnikov’s honey bee (Apis koschevnikovi).
Bumble bee (Bombus)
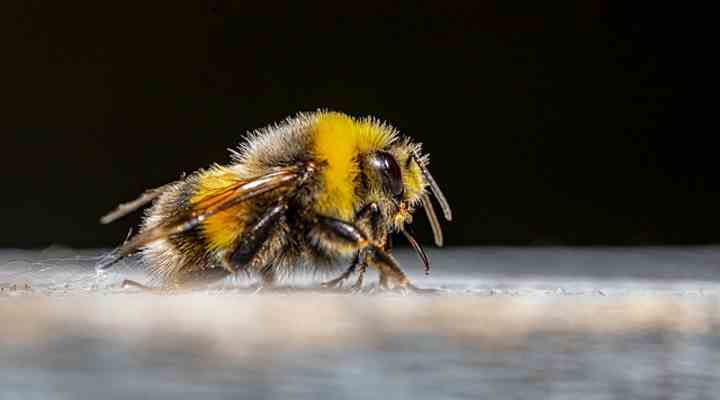

Bumble bees fly clumsily and can be identified by their fuzzy appearance and large black and yellow body with a white tail
The bumblebee is a large flying insect that resembles a big honeybee and it can be identified by its furry body and distinctive yellow and black bands. You will often find bumblebees feeding on pollen and nectar that they take back to their nests. However, bumblebees don’t make quantities of honey like honeybees.
Unlike honey bees, bumble bees live in nests and smaller colonies. They only store small amounts of food in the nest. Also, bumble bees have a wider body and fuzzier appearance compared to honey bees. Similar to honey bees, bumble bees have pollen sacs on their hind legs.
The name bumble bee literally means to buzz, hum, or move clumsily. This descriptive name accurately depicts their bumble behavior as they feed on flower pollen and nectar.
Bumblebees generally grow around 0.6” (17 mm) long.
Carpenter bee (Xylocopa, Ceratina)
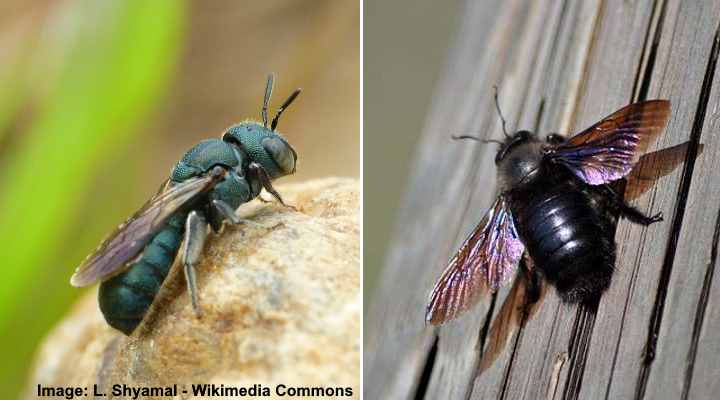

Left picture: The small carpenter bee (Ceratina). Right picture: The large black carpenter bee (Xylocopa)
Carpenter bees are big black flying insects that look like bumblebees only without the characteristic yellow bands. They include two types: The large carpenter bee (Xylocopa) which is a big black bee with fuzzy thorax, a shiny body, six legs, and two pairs of wings. The small carpenter bee (Ceratina) also has characteristics of carpenter bees, but they have a slender greenish-black metallic body.
Carpenter bees have the habit of burrowing into dead wood to create nesting tunnels. They can cause property damage if they drill into wood structures to create nests and lay eggs. Big black bees don’t live in colonies like bumblebees. For example, carpenter bees are solitary insects, and there is only one female in a nest.
Large black carpenter bees measure 0.7” (20 mm) long.
Mason bee (Osmia)
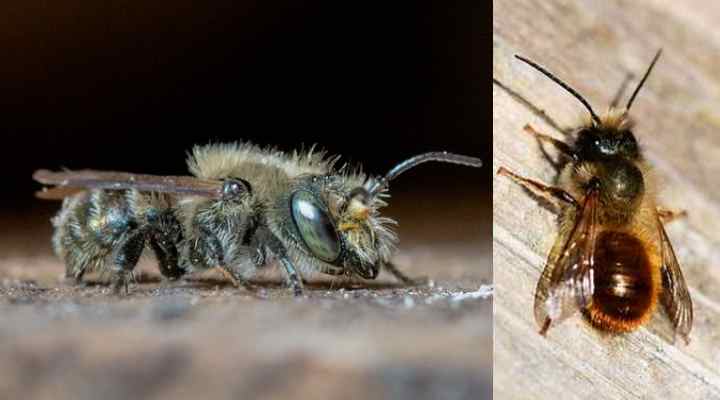

Many mason bees have metallic blue-green bodies (left picture). Some mason bees such as the red mason bee (Osmia bicornis) can have black or maroon colors (right picture)
Mason bees are common flying insects with metallic green or blue colors and patches of hair on their abdomens. Some mason bee species can be a reddish-brown color. The solitary bees nest in tubular cavities, often in abandoned insect nests. Like many other bees, mason bees are excellent pollinators.
Mason bees grow about 0.5” (13 mm) long.
Related reading: Insects that are easy to mistake for bees.
Wasps (Hymenoptera)
Wasps are a group of common flying insects with a recognizable smooth, slender body covered in black and yellow bands. One of the characteristic features of all wasps is the slim waist between the abdomen and thorax. Although most species of wasps are yellow and black, some are red, black, or brown.
Here are some common species of wasps.
European paper wasp (Polistes dominula)

European Paper Wasp (Polistes dominula)
Paper wasps are flying ‘bugs’ that have slender, elongated black bodies and broad yellow bands around the abdominal area. Female paper wasps also have yellow spots on their black head and thorax. An identifying feature of paper wasp is its orange antennae. These paper wasps tend to be aggressive flying insects and can inflict a nasty sting on humans.
The European paper wasp grows 0.3” to 0.5” (8 – 13 mm) long.
Yellowjackets (Vespula spp.)
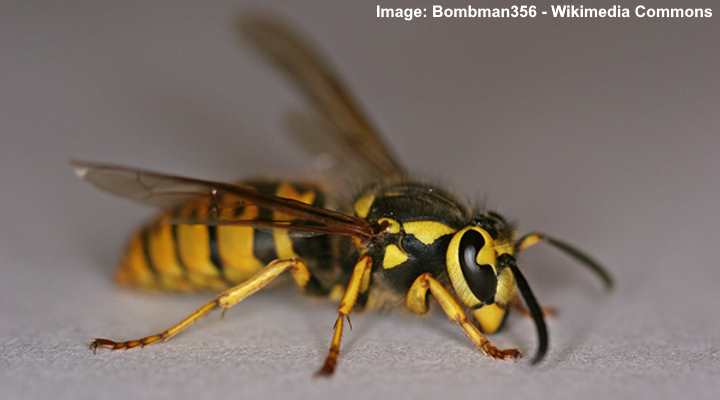

Eastern Yellowjacket (Vespula maculifrons)
Yellowjackets are identified as black and yellow flying insects with six yellow legs. The wasp’s smooth body helps to tell them apart from the common bumblebee or honeybee. It is also easy to mistake yellowjackets for aggressive hornets; however, they are much smaller. You will find yellowjackets nesting in holes, cracks, or crevices.
Eastern yellowjackets (Vespula maculifrons) are the typical black and yellow wasps that commonly become a pest in gardens.
Yellowjackets measure around 0.5” (13 mm) long.
Hornets (Vespa)
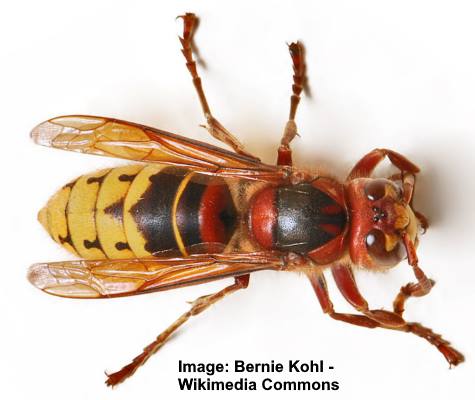

European Hornet (Vespa crabro) has reddish-orange wings
A hornet is a type of giant wasp with a large, striped body and dark brown and orange or yellow bands. There are three species of hornet, but the European hornet is the most prevalent in North America. The giant hornet has a reddish-brown head and thorax and a yellow and brown body.
These enormous wasps can be aggressive when they feel threatened. You can recognize a hornet because it looks like a giant wasp 1” to 1.4” (25 – 35 mm) long.
Common Flying Insects in the House
Flying insects are common indoors, where they are usually annoying pests. One of the most common flying insects in the house are flies. The concerning thing about household flies is that they can carry disease. Some household flies, such as fruit flies and gnats, are tiny flies seen near plants or decaying fruit.
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster)

Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster)
The common fruit fly is a tiny brown flying insect about 0.1” (2.5 mm) long. The flies are so small that it’s hard to distinguish their identifying features. But you will often see the tiny brown flies hovering over decaying fruit, garbage cans, or other rotten produce.
Drain fly (Psychodidae)
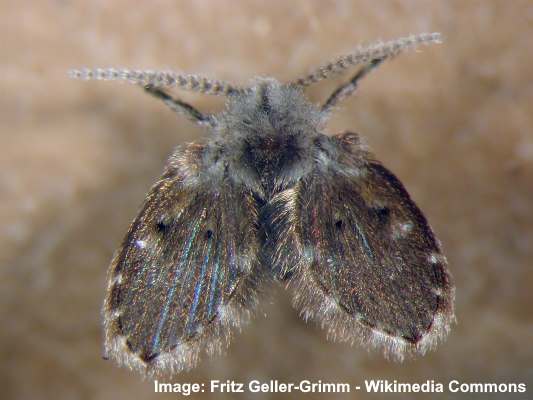

Drain flies (Psychodidae) have short furry bodies and wings
Also called sink fly, sewer gnat, or sewer fly, the drain fly is a grayish moth-like flying ‘bug’ with a short, stumpy body. As the name suggests, drain flies typically live in sinks and the sludge accumulated in drains. The small gray flies measure around 0.1” (2.5 mm) and usually emerge at night.
Fungus gnat

Fungus gnats (soil gnats) are soil dwelling small black houseplant pests that feed on fungus
The fungus gnat is a tiny black flying insect, identified by its behavior around houseplants. The black flying ‘bugs’ have dark wings and tend to fly when infected plants are disturbed. Although they are not harmful to plants, the flies can be annoying as they fly around your face. Fungus gnats measure 0.08” to 0.3” (2 – 8 mm) long.
Further reading: How to Get Rid of Gnats on Houseplants.
Housefly (Musca domestica)
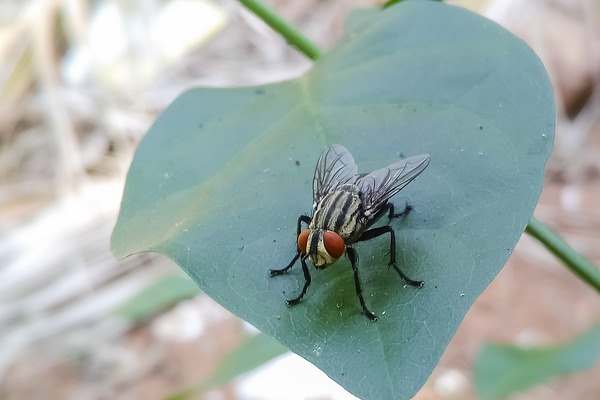

Houseflies (Musca domestica) are common house bugs that can cause infestation in large quantities
A housefly is a common flying pest and one of the most common insects in the world. The small oval flies are a nuisance and feed on rotten meat, fruit, and vegetables. The common housefly measures about 0.23” (6 mm) long. Houseflies are house bugs that are known to carry diseases and transmit bacteria.
Blowfly (Calliphoridae)
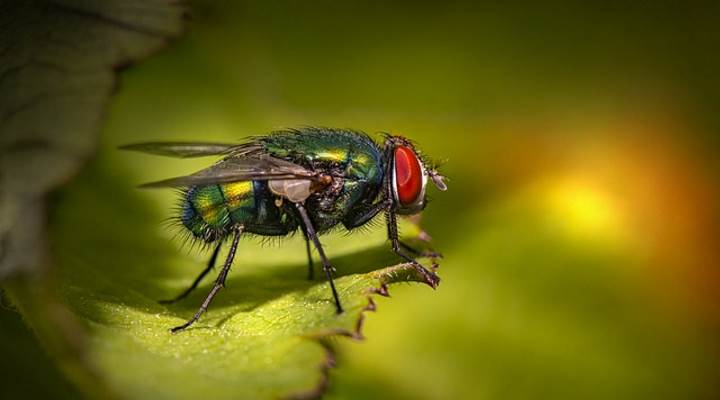

Blowflies (Calliphoridae) are usually shiny metallic in their appearance
A blowfly is a large, metallic gray, blue, or black fly. The annoying flying insects measure 0.3” to 0.4” (8 – 10 mm) and act like houseflies. Unfortunately, the disease-carrying flies feed on decaying flesh, feces, and rotten organic matter. Therefore, it’s vital to keep these nasty bluebottle flies out of your home.
Hoverflies (Syrphidae)

There are different species of hoverflies with various body patterns that look like bees
Hoverflies are a large group of flying insects that look like bees or wasps. The small flies have a smooth, slender abdomen with black and yellow bands. Depending on the species, the pollinating insects measure 0.25” to 1.25” (6 – 32 mm). You will often see the harmless wasp-like insects hovering near flowers during summer.
Hoverflies have one pair of wings, whereas bees and wasps have two pairs.
Butterflies (Lepidoptera)

Butterflies come in a huge range of colors and sizes and are active during the day
Butterflies are a beautiful and diverse group of flying winged insects. Individual species of butterflies are identified by their colorful wings that can have intricate patterns, iridescent colors, and conspicuous eye-like markings. An identifying feature of butterflies is their two clubbed antennae. You can easily spot butterflies as they flutter around flowers in summer gardens.
Butterflies range in size from tiny, winged insects with a wingspan of 0.13” (3.2mm) to giant flying insects measuring 12” (300 mm) across.
Moths
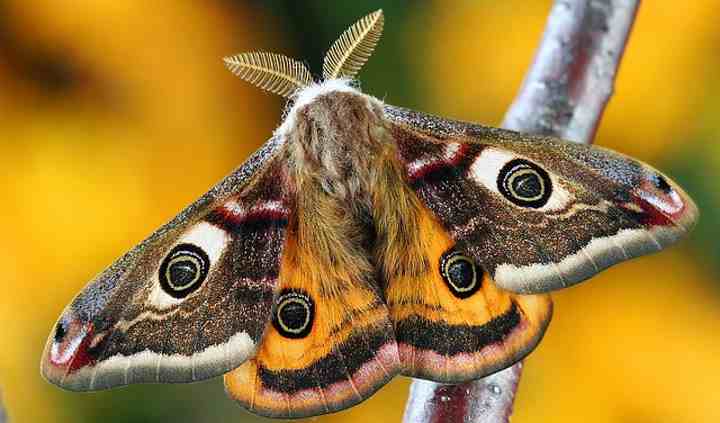

Moths can be identified by their feathery antennae, nocturnal activity and holding their wings parallel to the ground when resting
Moths are a group of flying insects, similar to butterflies, that typically come out at night. Although most moths have unremarkable grayish or brown wings, some spectacular moth species can be as stunning as butterflies. Moths have feathery antennae and tend to have furry bodies and blend in more with their surroundings. Some moths look like leaves, whereas other moths have bright colors to ward off predators.
Related reading: Types of moths.
Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae)

The tiny whitefly is a pest that can usually be found on the underside of the plant’s leaves
Whiteflies are tiny white flying bugs that are no more than 0.08” (2 mm) long. Like all bugs, the white flying insects feed on plant tissue by sucking the leaves and stem juices. In addition, while feeding, the white-colored flies inject saliva that can spread plant diseases. A large number of whiteflies can quickly take over a plant, causing weakened growth.
The flying white bugs can be a significant pesky insect on houseplants and in greenhouses.
Related reading: How to get rid of whiteflies on plants.
Mosquitoes (Culicidae)
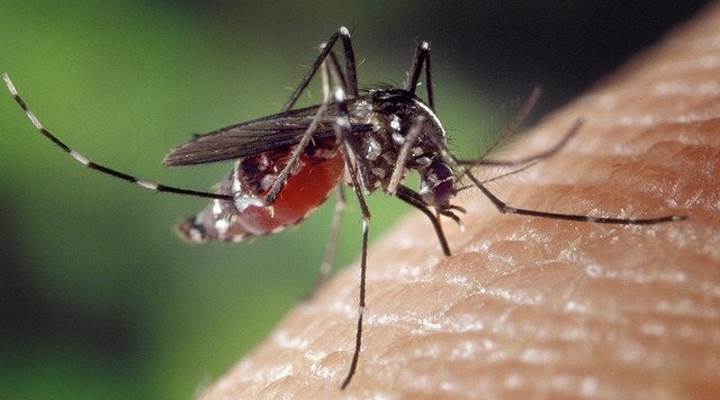
Mosquitoes are bloodsucking insects with one pair of wings, slender body and 3 pairs of long legs
Mosquitoes are tiny flying insects that are famous for their bloodsucking habits. Mosquitoes have slender bodies measuring 0.1” to 0.7” (2 to 19 mm) long. Mosquitoes are pesky flying insects that usually come out at dusk, looking for a blood meal. In many tropical and subtropical countries, mosquitos are dangerous insects because they transmit diseases like malaria, Zika, and dengue fever.
Ladybugs (Coccinellidae)

Ladybugs have a pair of hardened wings (called elytra) that protect the pair of flight wings underneath
Ladybugs are colorful flying insects that are a type of beetle. Ladybugs are identified by their red, yellow, or orange oval-shaped body with black spots. In addition, it’s possible to identify some species of ladybugs by the number of dots on their colorful wings. Also called ladybirds, the small beetles measure between 0.03” and 0.7” (0.8 – 18 mm) long.
Ladybugs are classified as beneficial insects, and they can help with pest control because they feed on scale insects and bugs like aphids.
Cockroaches (Blattodea)
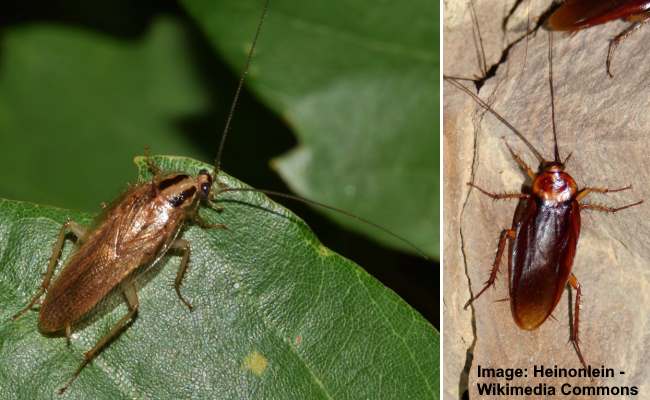

Common roach (German roach/Blattella germanica) on the left and American roach (Periplaneta americana) on the right
Most species of cockroaches have wings, and some are classified as brown flying insects. Although cockroaches are famous for scurrying over surfaces when you turn on the light, some are adept flyers. For example, the Asian cockroach, Australian, and Pennsylvania wood cockroach are also excellent flyers. However, because they are generally nocturnal, they are hard to spot and eradicate.
All types of cockroaches are disease-carrying insects, and it’s vital to get rid of them from your home.
Black Flying Beetles
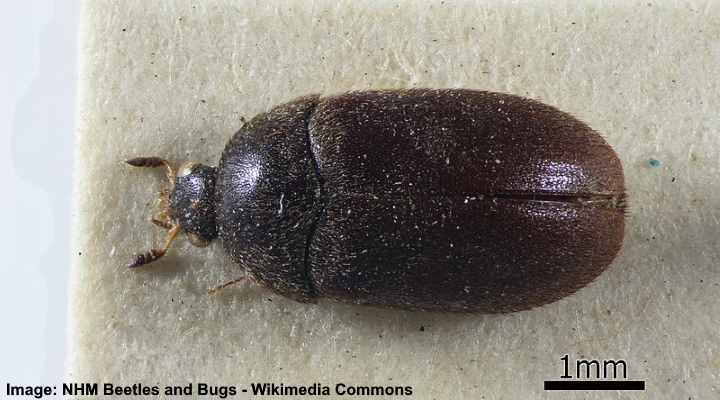

The small black flying carpet beetle is an indoor invasive pest
All beetles have wings, and most species can fly. However, some black flying beetles can become an invasive ‘bug’ in homes. For example, the carpet beetle, drugstore beetle, and flour beetles can fly into your home. These tiny annoying pests can then infest soft furnishings and dried food items. In addition, some larger flying beetles, such as June beetles, Japanese beetles, and click beetles, can fly from nearby gardens and infest plants in your yard.
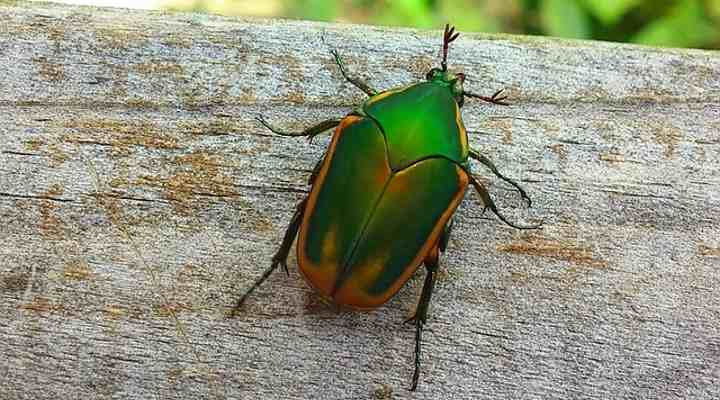

The Green June Beetle is a common green insect in early summer
Related reading: How to get rid of Japanese beetles from your yard.
Dragonflies

Dragonflies are agile flying insects and most of them live in tropical areas
A dragonfly is an unusual flying insect with a long, colorful, stick-like body, large transparent wings, and two large compound eyes. Dragonflies are identified by their metallic or iridescent red, blue, and green colors. Depending on the species, dragonflies measure between 1” and 4” (25 – 101 mm) with a wingspan of 2” to 5” (51 – 127 mm).
You will often find dragonflies resting on flowers, sitting on stagnant water, or hovering over streams or rivers.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys)

Stink bugs are generally brown flying insects with some color variation depending on the species
Stink bugs are one of the few types of true bugs capable of flying. The stink bug is identified by its form in the shape of a shield. The flying bug looks dark brown and has six legs and two dark antennae with yellow bands. Stink bugs emit a characteristic foul odor as a defense mechanism.
Although they generally crawl around plants and vegetation, destroying foliage, the bugs can fly. Swarms of the bugs may fly to new locations. You may also see the large bugs flying around light fixtures in the evening.
Related articles:
