Types of Elm Trees: Leaves, Bark, Seeds – Identification Guide (Pictures)

Elm trees are a species of deciduous and semi-deciduous trees in the genus Ulmus. A common feature of most elm trees is their oval-shaped leaves with toothed edges, a pointed end, and visible veins.
Elm trees are huge shade trees that can grow up to 100 ft. (30 m) tall with a wide spread of around 75 ft. (22 m). Some elm species have tall, upright growth, and other types of elm trees have an umbrella-shaped canopy.
There are 35 species of elms, eight of which are native to North America. The greatest diversity of elm trees is in the tall, bushy trees that are classed as Asiatic elms. These native elms are found in China, India, eastern Siberia, and Central Asia.
Find out about ways to identify the different species of elm trees by looking at their bark, leaves, and other features.
Elm Tree Facts
Elm trees are a common type of large tree that has a wide, spreading canopy. Elms are popular trees for providing shade in backyards, along residential streets, or in parks.
The distinguishing feature of elms are their deeply ridged bark and pointed oval leaves with serrated edges. Elms are also a species of flowering trees. After blooming in spring, the elm tree flowers produce seeds encased in an oval papery structure called a samara.
Elm tree wood is also important in the timber industry. Elm timber is strong, resistant to rot and splitting, yet is still flexible. Elm wood is used for making ship keels, archery bows, furniture, and musical instruments.
Elms are often associated with Dutch elm disease—a fungal infection growing in the tree’s sapwood. Due to this disease, the majority of American elms (Ulmus americana) were almost wiped out. To protect the spread of Dutch elm disease, it’s vital to identify sick elms and remove them, so they don’t infect other elms in the neighborhood.
Many new species and varieties of elm trees are more resistant to Dutch elm disease.
Elm Tree Leaves
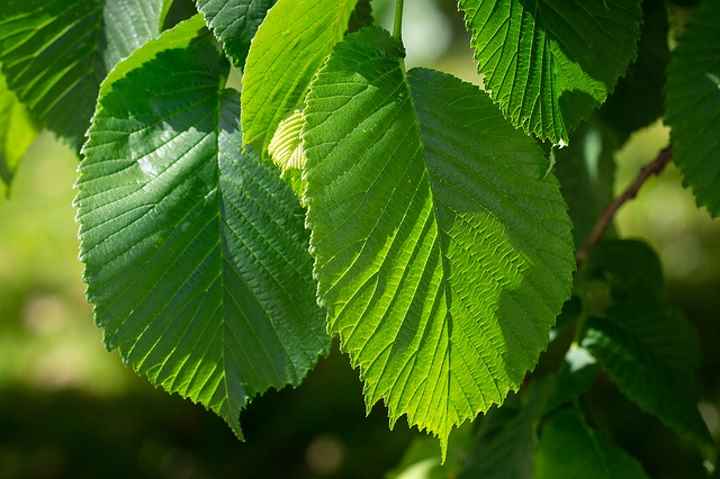

Elm leaves have oval shape, jagged edges, pointed tip and visible veins
Elm leaves are oval with jagged edges, pointed end, and visible green veins. One half of the elm leaf is shorter than the other, giving the jaggy leaf blade a somewhat lopsided look.
Most elm tree leaves are between 4” and 6” (10 – 12 cm) long and up to 2.5” (7 cm) wide.
Most species of elms have light green to dark green leaves. These leaves turn a golden yellow or dull yellow color in the fall, depending on the species.
Elm Tree Bark
Elm bark is a dark grayish-brown color with deep furrows and a scaly appearance. These deep fissures run vertically and intersect with each other. Common names of some elm trees such as ‘lacebark elm’ describe the lace-like textures on the tree trunk and branches.
Elm Tree Seeds

Seeds of elm tree
Elm tree seeds are small and round and are protected in an oval papery casing called a samara. Each light green elm samara contains a single seed, and they grow in clusters. The elm seeds form after flowering and disperse from the tree in spring.
Elm Tree Identification
Elm trees can be identified by their gray bark with deep furrows, pointed oval leaves that have double-serrated margins, and their large sprawling canopy. Elm flowers are inconspicuous clusters of flowers appearing in spring that mature into round samaras, or elm seeds. Elm foliage turns golden yellow in the fall.
Types of Elm Trees (With Pictures) – Identification Guide
American Elm (Ulmus americana)
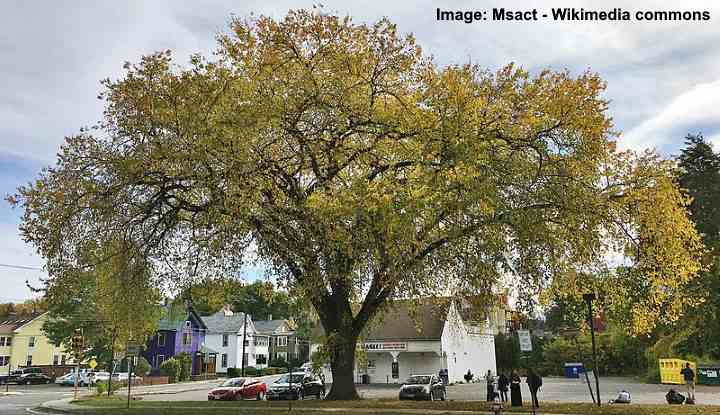
American elm (tree overview)
The American elm tree is a large deciduous tree with an umbrella-like canopy. American elms—also called white elms or water elms—grow to 80 ft. (24 m) tall with a broad-rounded crown about 75 ft. (22 m) wide. Once a common shade tree, the American elm has lost popularity due to its susceptibility to Dutch elm disease.
Elm tree bark
American elm bark is grayish-brown, with deep diamond-shaped fissures, and broad ridges.
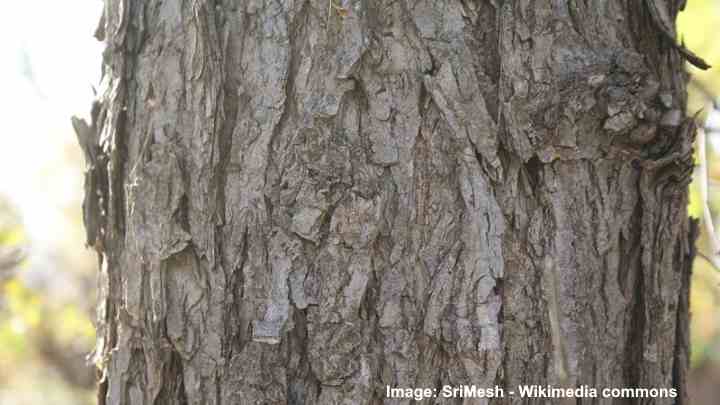

American elm bark
Elm tree leaves
American elm leaves are ovate in shape and are 3” to 5” (7.5 – 13 cm) long and up to 3” (7.5 cm) wide. These green elm leaves have double-serrated uneven edges. The blade surface is smooth and has visible veins.
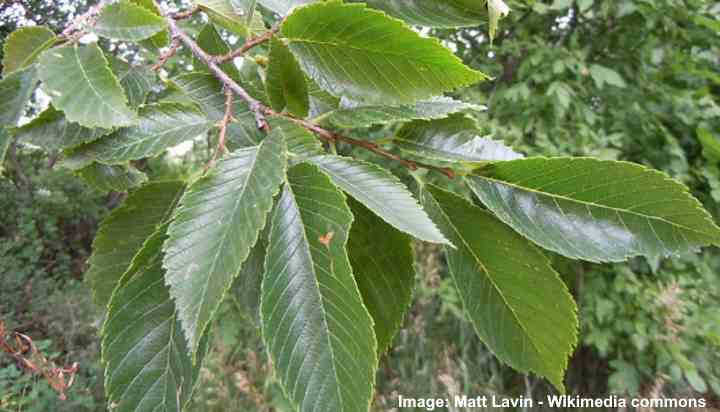

American elm leaves
Florida Elm Tree (Ulmus americana var. floridana)
The Florida elm is a fast-growing tree that is smaller than the American elm. Florida elms have a vase-shaped growth with foliage made up of ovate leaves that have typically serrated margins. The bark is similar in color and texture to the American elm.
Chinese Elm Tree (Ulmus parvifolia)

Chinese elm tree and leaves
Chinese elms are small deciduous or semi-deciduous trees with a slender trunk and bushy crown. Also called lacebark elms or drake elms, Chinese elm trees grow to between 33 and 60 ft. (10 – 18 m) tall. These species of elms are popular as ornamental landscape trees or shade trees.
Drake elms, or Chinese elm trees, are popular because they’re more resistant to Dutch elm disease than other Ulmus species.
Elm tree bark
Chinese elm trees have distinctive flaking bark that reveals small thin patches of orangey bark underneath.
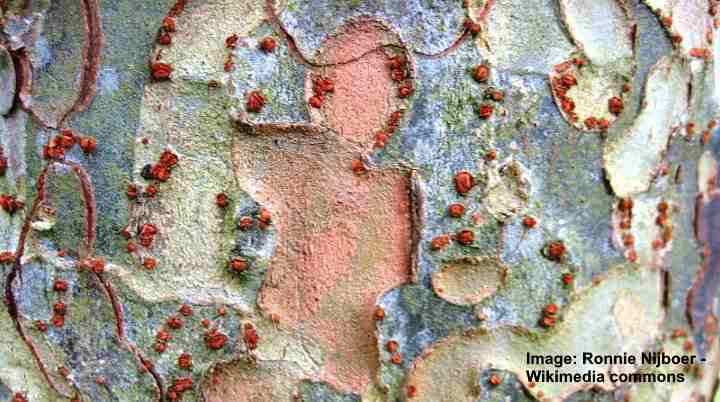

Chinese elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Chinese elm leaves are small and leathery with single-toothed margins.
Bosque Elm Tree (Ulmus parvifolia ‘Bosque’)
Bosque elms are a cultivar of the Chinese elm and are tall, graceful trees with an oval canopy and branches that slightly droop. The Bosque elm is a popular shade tree in parks and along residential streets. Interesting features of this elm tree cultivar are its peeling bark and golden-red leaves in the fall.
Bosque elm is a small tree that is usually less than 6 m (20 ft.) tall and is a fast growing tree.
Cedar Elm Tree (Ulmus crassifolia)

Cedar elm tree (bonsai) and leaves
The cedar elm—also called Texas elm tree—is a large deciduous tree native to North America. The Texas cedar elm grows up to 82 ft. (25 m) tall. Its green leafy foliage creates a spreading rounded crown. Cedar elms are large trees with small oval green leaves and rough bark.
Although Texas elms drop their leaves in the fall, in some growing zones, the elms are semi-deciduous or evergreen.
Other common names of cedar elm are basket elm, scrub elm, southern rock elm, or lime elm.
Elm tree bark
Cedar elm tree bark is gray and scaly with medium fissuring on the trunk.

Cedar elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Texas cedar elms have the smallest leaves of any North American native Ulmus species. Jagged-edged leaves are up to 2” (5 cm) long and 0.7” (2 cm) wide.
Siberian Elm Tree (Ulmus pumila)
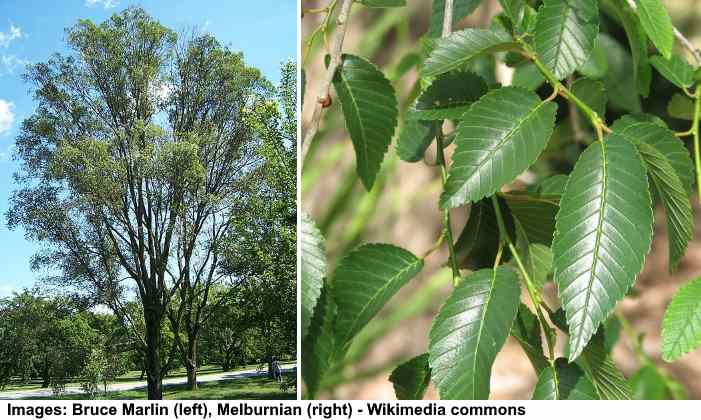

Siberian elm tree and leaves
Siberian elm trees are small to medium-sized bushy trees with a rounded crown of dense foliage. The tree is also called the Asiatic elm or dwarf elm and is sometimes confused with the Chinese elm. Siberian dwarf elms grow to between 50 and 70 ft. (15 -21 m).
Distinctive features of Siberian elms are small red flowers, winged seeds, and brittle branches that break easily.
Elm tree bark
Siberian elm bark is gray with fissures running vertically up the trunk.

Siberian elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Siberian elm tree leaves are shiny dark green with typically serrated margins. The elm leaves are 3” (7 cm) long and 1.2” (3 cm) wide.
Japanese Elm Tree (Zelkova serrata)

Japanese elm tree and leaves
Japanese elms (Zelkova serrata) are large deciduous trees with a broad canopy and rounded shape. The fast-growing elms are identified by their short trunk that splits into many spreading branches. The large shrubby elms grow up to 55 ft. (16 m) tall.
Japanese elm trees are popular ornamental landscape trees for shade as they are resistant to Dutch elm disease.
Elm tree bark
The bark of Japanese elms is smooth compared to other species of elms. The bark color is grayish-brown to grayish-white and can be flaky.

Japanese elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Japanese elm leaves are an oblong-ovate shape with toothed margins. The small light green elm leaves have a rounded base and typically pointed tip.
Cherry-Bark Elm (Ulmus villosa)
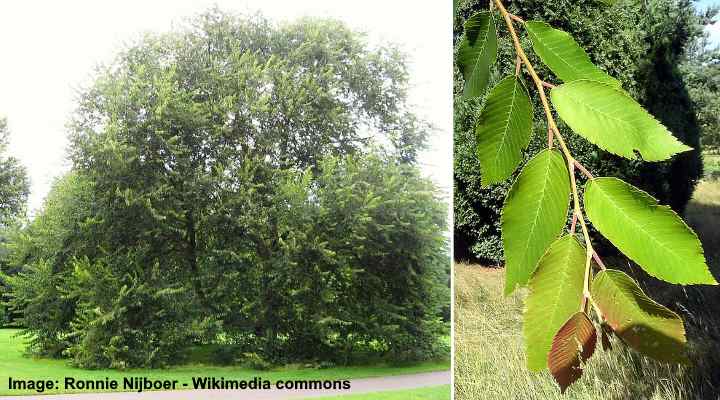

Cherry bark elm tree and leaves
Cherry-bark elm trees or Marn elms are large bushy trees that grow up to 82 ft. (25 m) tall and have a rounded shape. The elm tree branches sometimes hide the smooth bark on the thick trunk. A distinguishing feature of cherry-bark elms is their elliptic rather than round samaras.
These long-leaved cherry-bark elm trees are somewhat resistant to Dutch elm disease and are popular as shade trees in parks.
Elm tree bark
Cherry-bark elms have bark that is smooth with bands of flaky bark wrapping around the trunk, similar to birch trees.

Bark of cherry-bark elm tree
Elm tree leaves
Cherry-bark elm trees have long oblong, bright green leaves with jagged-looking edges. The elm leaves are up to 4” (11 cm) long and 2” (5 cm) wide and have a pointed tip, characteristic of elm leaves.
Wych Elm Tree (Ulmus glabra)
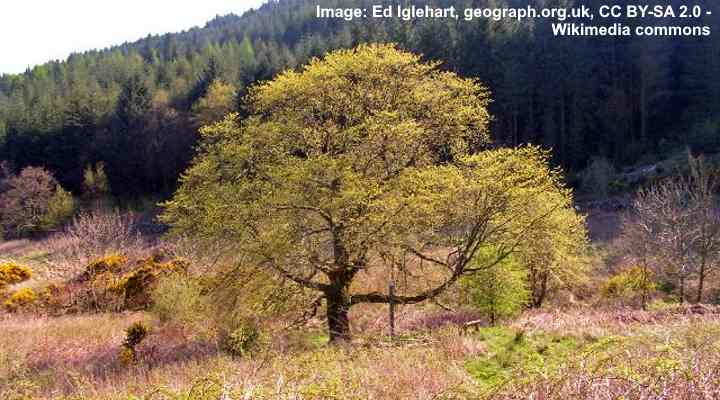

Wych elm tree overview
The wych elm or Scotch elm is a native European elm species with a sizeable umbrella-type canopy. Scotch elms can grow up to 130 ft. (40 m) and most of this height is the massive rounded crown. The deciduous elm is cold-hardy and is found in many Northern European countries.
Wych elms are characterized by short fat trunks, spreading branches, and winged samaras.
Elm tree bark
Wych elm bark is gray and smooth when young, which gradually develops fissures as the tree matures.
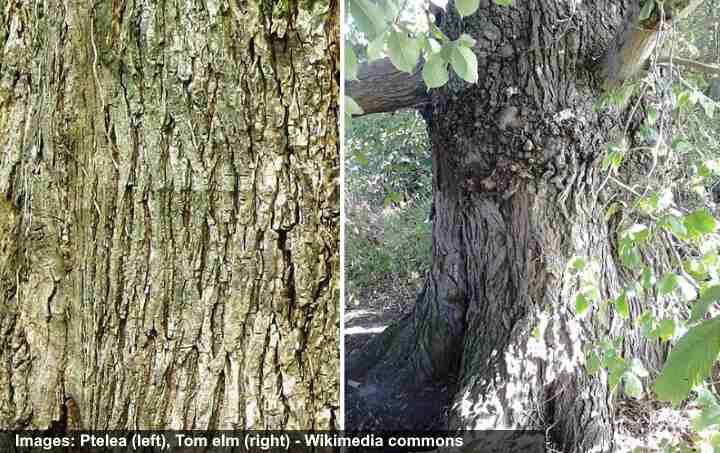

Wych elm bark of mature tree
Elm tree leaves
Scotch elm leaves are long, broad, with ovate shaped blades. The large lime-green elm leaves are up to 6.5” (17 cm) long and 5” (12 cm) wide.
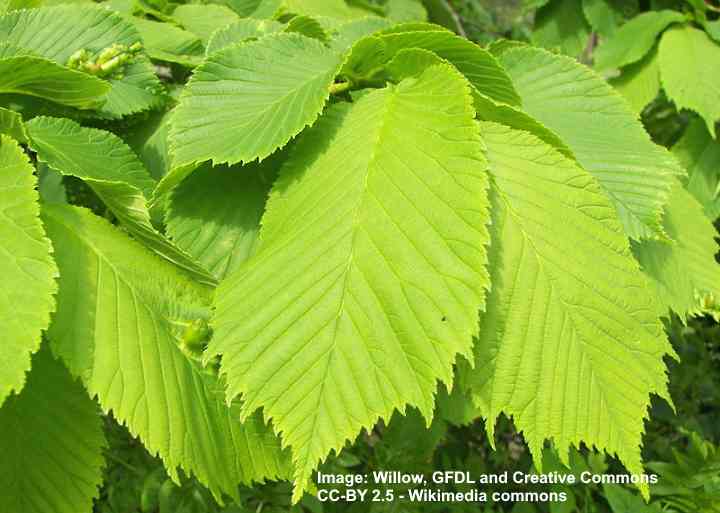

Wych elm leaves
Golden Wych Elm (Ulmus glabra ‘Lutescens’)
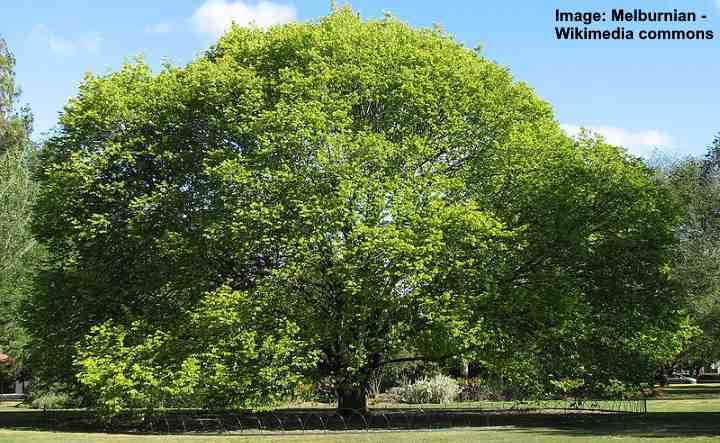

Golden wych elm tree overview
Golden wych elms are a smaller cultivar of the species Ulmus glabra. This elm is a medium-sized deciduous tree, growing to no more than 50 ft. (15 m) and with an umbrella-type canopy that is 65 ft. (20 m) wide.
A distinguishing feature of this wych elm cultivar is its bright yellow leaves when growing in full sun.
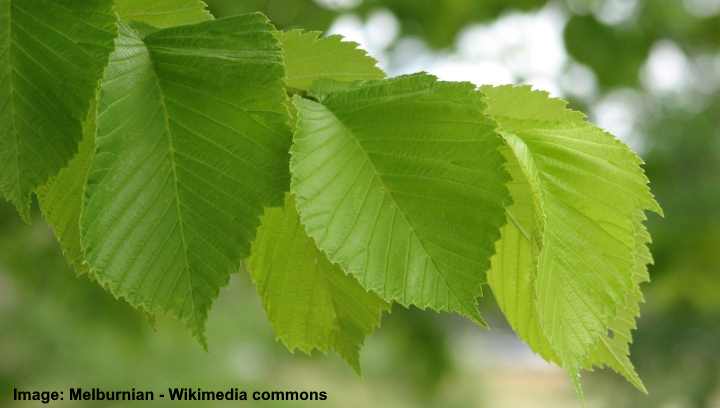

Golden wych elm leaves
Camperdown Elm Tree (Ulmus glabra ‘Camperdownii’)
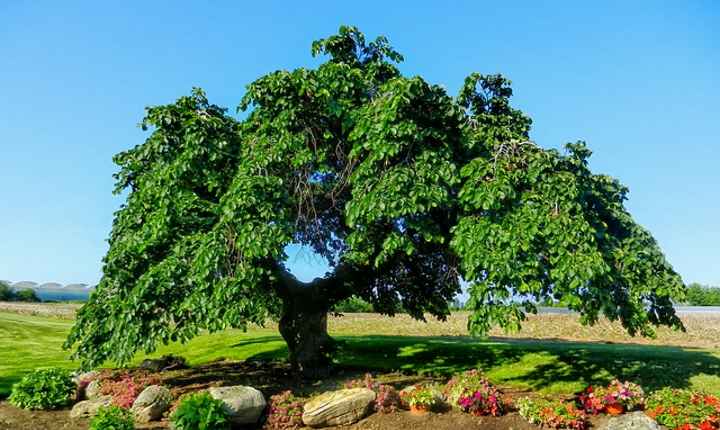

Camperdown elm tree
The Camperdown elm cultivar has drooping branches that give it another common name – ‘weeping elm.’ Unlike other elms, the Camperdown elm has a flat canopy and pendulous branches. This weeping elm grows to between 15 and 25 ft. (4.5 – 7.5 m) tall.
Elm tree bark
Camperdown elm tree bark is grey and smoother than that of the English elm and covers a straight, upright trunk.
Elm tree leaves
Leaves growing on Camperdown elms are broad, double-toothed, veined, and rough to touch. Weeping elm leaves are up to 6” (15 cm) long and turn dull yellow in the fall.

Camperdown elm leaves and seeds
English Elm (Ulmus procera)
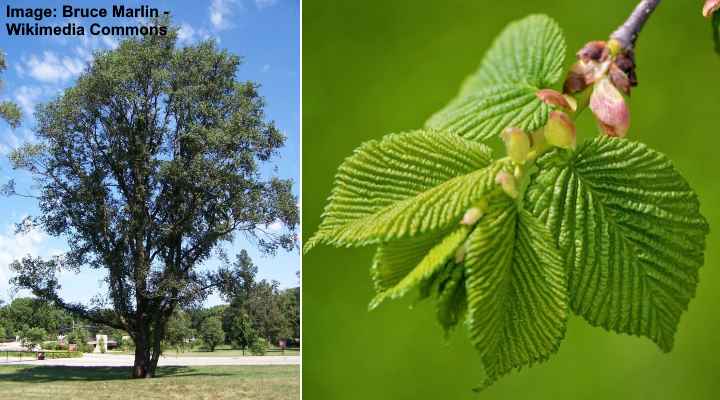

English elm tree and young leaves
English elm trees are huge deciduous elms with rough bark and coarse leaves. Although English elms are large shade trees, they can also be used in hedgerows or grown as large tree-like shrubs in backyards. Mature English elms grow to 100 ft. (30 m) tall.
Elm tree bark
English elm bark is rough and fissured with a grayish-brown color.
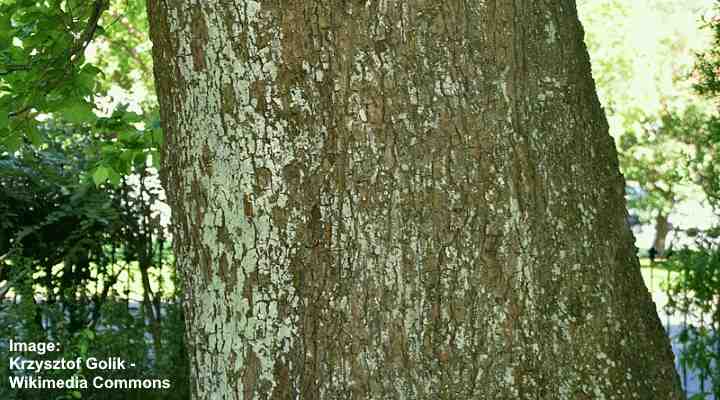

English elm bark
Elm tree leaves
English elm leaves are dark green, with serrated margins, and an asymmetrical base. These elm leaves are smaller than wych elms and are between 1.5” and 3.5” (4 – 9 cm) long.
Field Elm (Ulmus minor)
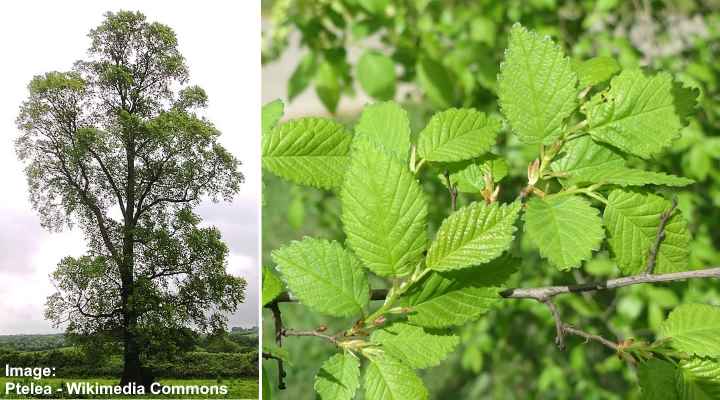

Field Elm tree and leaves
Field elm trees can be identified by their tall, graceful stature, small leaves, and rough trunk. The elm tree’s botanical name Ulmus minor refers to its small oval, glossy green leaves. Field elms can reach up to 100 ft. (30 m) tall.
Elm tree bark
Field elms have rough, furrowed bark that looks like blocks on the tree trunk. This elm tree species has gray-brown bark.

Field elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Field elm trees have small, smooth leathery leaves with an asymmetrical base and pointy end. The double-toothed ovate leaves grow to between 2.3” and 6” (6 – 15 cm) in length.
English Elm ‘Atinia’ (Ulmus minor ‘Atinia’)
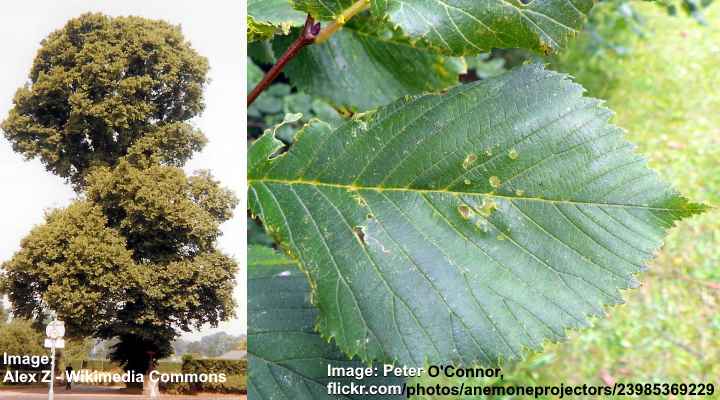

English elm ‘Atinia’ tree and leaves
The English elm cultivar ‘Atinia’ also goes by the name common elm or just English elm. This fast-growing elm is one of the largest deciduous trees in Europe. Huge English elms are around 130 ft. (40 m) tall with a thick trunk that’s 6.5 ft. (2 m) in diameter. This English elm’s distinctive feature is its ‘figure-of-eight’ foliage shape.
Elm tree bark
The Atinia elm bark is whitish-gray with shallow furrowing and a slightly scaly appearance.
Elm tree leaves
English elm ‘Atinia’ leaves are almost oval with a pointed tip, typical of all elm leaves. Look for teeth-like edges on the blade that point upward and an asymmetrical base.
Slippery Elm Tree (Ulmus rubra)
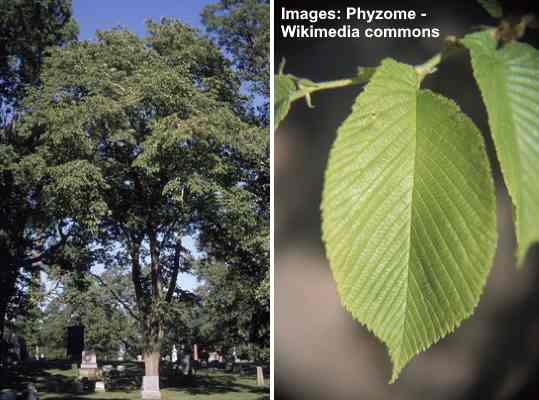

Slippery elm (red elm) tree and leaves
Slippery elms are a medium-sized species of Ulmus native to North America. The other common names for slippery elms refer to distinct characteristics of the tree. For example, gray elm, soft elm, or red elm, describe the color and soft texture of parts of the bark.
Slippery elms are similar in appearance to American elms. The difference between slippery or red elms and American elms is their red inner bark, chestnut-brown buds, and fuzzy twigs. Red or slippery elms are also smaller than American elms, only growing to between 40 and 62 ft. (12 – 19 m).
Slippery elm is a common herbal remedy that is made from the elm’s mucilaginous inner bark. Native Americans also used slippery elm’s red bark in traditional medicine—so, the species is also called the Indian elm.
Elm tree bark
Slippery elm has reddish-gray bark with long shallow furrows and a scaly appearance.

Slippery elm bark
Elm tree leaves
Red elm leaves are long obovate with a rough upper side and a smooth, velvety underside. As with all elm tree leaves, serrated margins identify these leaves. Slippery elm leaves start as a red color, turn to dark green, then become dull yellow in the fall.
European White Elm (Ulmus laevis)
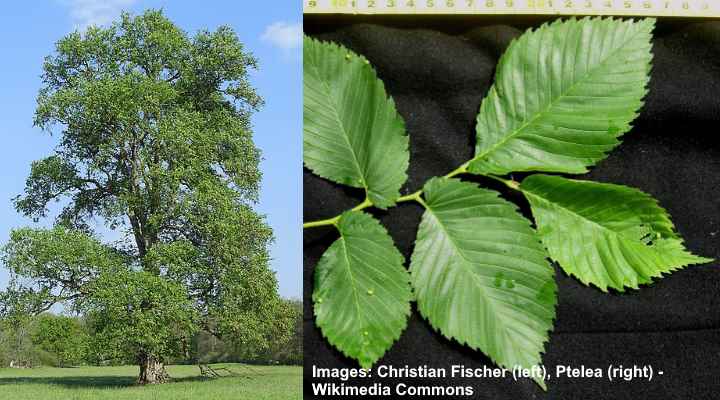

European white elm tree and leaves
European white elms are deciduous trees with a rounded crown and a loose branch formation. The European white elm is a large tree growing up to 100 ft. (30 m). This species of elm looks similar to another native European tree, the wych elm.
The European white elm’s distinguishing feature is the fact it’s one of the first elm trees to lose its leaves in the fall.
Elm tree bark
The bark of European white elms is whitish-gray and smooth when the trees are young. As the elms age, the grayish bark becomes slightly fissured and scaly with hints of reddish-brown bark.

European white elm bark (bark of old tree)
Elm tree leaves
European white elm leaves are ovate shaped with the typical elm toothed edging and lopsided look.
Dutch Elm (Ulmus hollandica)
Dutch elm trees are hybrids between wych elms (Ulmus glabra) and field elms (Ulmus minor). Dutch elm hybrids are massive shade trees, growing up to 130 ft. (40 m). There are many cultivars of this elm hybrid, and most have a conical shape, light-colored foliage, and serrated ovate leaves.
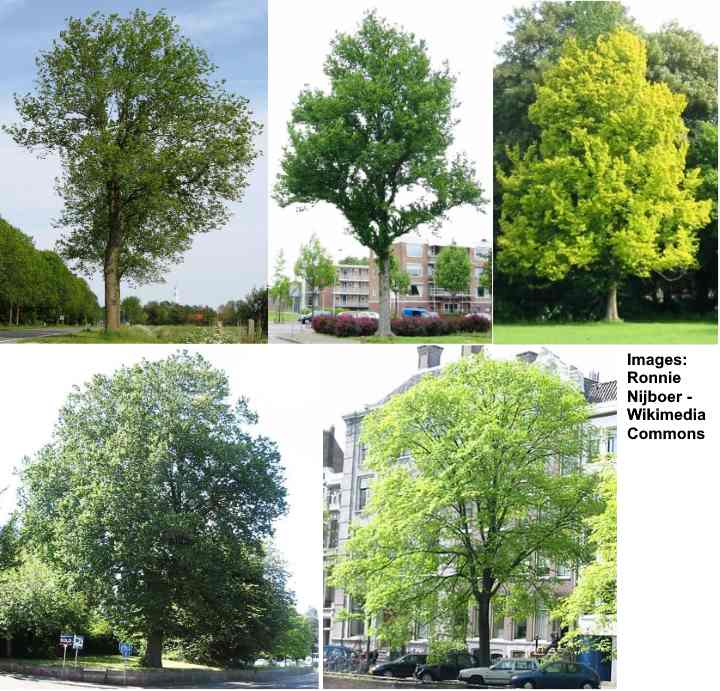

Dutch elm various cultivars. From top left clockwise: ‘Commelin’, ‘Dampieri’, ‘Wredei’, ‘Belgica’ and ‘Major’ cultivars
Related articles:
